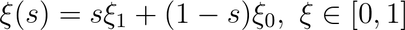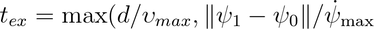Holonomic Vehicle Boundary Value Solver
Explicit solutions to the problem of point-to-point navigation of a holonomic vehicle operating within an obstacle-free world are straightforward. More specifically, a 6-degrees of freedom (DOF) vehicle that can be approximated to assume only small roll and pitch angles can be approximated using a very simple Boundary Value Solver (BVS). Considering an approximate state vector ξ = [x,y,z,ψ] (where x,y,z are the 3 position states and ψ the yaw angle), the path from the state configuration ξ0 to ξ1 is given by:
And considering a limitation on the possible rate of change of the yaw angle \dψ/dt|max and the maximum linear velocity υmax, the execution time is:
with d used to denote the Euclidean distance.
Python Implementation
File: HoverModeMain.py
# __HOVERMODEMAIN__ # This is the main file to execute examples of the Hover mode # # Authors: # Kostas Alexis ([email protected]) from HoverFunctions import * from PlottingTools import plot3 import numpy as np import time import sys pi = np.pi verbose_flag = 0 plot_flag = 1 point_0 = np.array([0,0,0,0]) point_1 = np.array([10,10,10,pi/4]) class ExecutionFlags(object): """ Execution flags """ def __init__(self, verbose_flag, plot_flag): self.verbose = verbose_flag self.plot = plot_flag class VehicleParameters(object): """ Vehicle Parameters """ def __init__(self, v_max, psi_rate_max): self.v_max = v_max self.psi_rate_max = psi_rate_max def main(): # Example main for the Hover mode t0 = time.clock() VehiclePars = VehicleParameters( 4, pi/4,) ExFlags = ExecutionFlags( verbose_flag,plot_flag ) flag_nc = 0 fname = 'hover_solution.txt' HoverSolution = AssembleHoverSolution(point_0, point_1, VehiclePars.v_max, VehiclePars.psi_rate_max) path_hover = HoverSolution['connection'] np.savetxt( fname, path_hover, delimiter = ',' ) if ExFlags.plot : print '### Hover solution plot' plot3( path_hover[:,0], path_hover[:,1], path_hover[:,2], 'o', 'g' ) def testAllCases(): main() print 'Press any button to continue' raw_input() if __name__ == "__main__": testAllCases()
File: HoverFunctions.py
# __HOVERFUNCTIONS__ # This is the main file to execute functions of the Hover mode # # Authors: # Kostas Alexis ([email protected]) from __future__ import division import numpy as np from math import tan, sin, cos, atan2, fmod, acos, asin, pow, sqrt, fabs,atan from ElementaryFunctions import max, min pi = np.pi HoverSolution = { } HoverSolution['connection'] = np.zeros((2,4)); HoverSolution['distance'] = 0; HoverSolution['t_ex'] = 0; def computeHoverConnection(point_0=None, point_1=None): L = np.array([point_0, point_1]) return L def computeHoverConnectionDistance(point_0=None, point_1=None): dist_ = sqrt( pow(point_1[0]-point_0[0],2) + pow(point_1[1]-point_0[1],2) + pow(point_1[2]-point_0[2],2) ) return dist_ def computeHoverConnectionTime(point_0=None,point_1=None,v_max=None,psi_rate_max=None): dist_ = computeHoverConnectionDistance(point_0, point_1) t_ex = max( dist_/v_max, fabs(point_1[3]-point_0[3])/psi_rate_max) return t_ex def AssembleHoverSolution(point_0=None,point_1=None,v_max=None,psi_rate_max=None): L = computeHoverConnection(point_0, point_1) dist_ = computeHoverConnectionDistance(point_0, point_1) t_ex = computeHoverConnectionTime(point_0, point_1, v_max, psi_rate_max) HoverSolution['connection'] = L HoverSolution['distance'] = dist_ HoverSolution['t_ex'] = t_ex return HoverSolution
File: PlottingTools.py
# __PLOTTINGTOOLS__ # Plotting functions # # Authors: # Kostas Alexis ([email protected]) import matplotlib.pyplot as mpplot from matplotlib import pyplot import pylab from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D def plot3(a,b,c,mark="o",col="r"): # mimic matlab plot3 from matplotlib import pyplot import pylab pylab.ion() fig = pylab.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.invert_zaxis() ax.invert_xaxis() ax.set_aspect('equal', 'datalim') ax.plot(a, b,c,color=col,marker=mark) fig.show()